















Salts or ions of the theoretical carbonic acid, containing the radical CO2(3-). Carbonates are readily decomposed by acids. The carbonates of the alkali metals are water-soluble; all others are insoluble. The conjugate base of HCO3- is CO32-. Conjugates always differ by one H+. A conjugate base has one fewer H+, while a conjugate acid has one more H+. Create your account. View this answer. The conjugate base of HCO 3 - is CO 3 -2, which is the carbonate ion. To determine the conjugate base of a substance, you remove one hydrogen ion. The carbonate ion carries a negative two formal charge and is the conjugate base of the hydrogen carbonate ion, HCO 3 −, which is the conjugate base of H 2 CO 3, carbonic acid. A carbonate salt forms when a positively charged ion attaches to the negatively charged oxygen atoms of the ion, forming an ionic compound . The hydrogen carbonate ion, HCO3, has both a conjugate acid and a conjugate base. These are, respectively: CO;2-, H2CO3 Онҳо*, он OH,CO3, C0,2- HCO3, HCO3 $ HCO3, HCO3 Get more help from Chegg The conjugate base of bicarbonate, HCO 3- is carbonate, CO3 2-.. HCO3- is a conjugate acid, H 2 CO 3 Hydrogen carbonate ion, HCO 3 –, is derived from a diprotic acid and is amphiprotic. Its conjugate acid is H 2 CO 3 , and its conjugate base is CO 3 2– . The use of conjugate acid-base pairs allows us to make a very simple statement about relative strengths of acids and bases. Furthermore, what is the conjugate base of hco3 −? Bicarbonate: HCO3 - is known as hydrogen carbonate or bicarbonate. It's a polyatomic ion that can bond to any positive ion. According to the Brønsted-Lowry theory of acids and bases, bicarbonate is a conjugate acid. The conjugate base of HCO3 - is CO3 -2, which is the carbonate ion. Answer and Explanation: When a proton is added to a carbonate ion, its conjugate base is formed. CO32−+H+⇌ HCO3− C O 3 2 − + H + ⇌ H C O 3 −. The conjugate base of carbonate ion is A conjugate acid is a substance that is formed when a base receives a proton, or H +. So, in order to determine the conjugate acid for a given base, all you have to know is that. base+H + → conjugate acid of that base. In your case, the base is hydrogen carbonate, or H CO− 3. If you write the equation you'll get.
[index] [2776] [2440] [5338] [8724] [4422] [2473] [6471] [9559] [468] [3658]
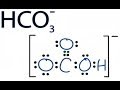
In the following equations water is acting as a proton acceptor. If the hydrogen carbonate ion is a common amphiprotic ion. In the presence of a strong base it can behave as a proton donor. In the ... In this video we'll balance the equation HCl + Ca(OH)2 = CaCl2 + H2O and provide the correct coefficients for each compound. To balance HCl + Ca(OH)2 = CaCl... This chemistry video tutorial explains how to calculate the pH of weak acids and bases such as HC2H3O2 and NH3 given Ka (acid dissociation constant) and Kb (... http://leah4sci.com/acidbase presents: Acidity of Aromatic compounds - Video 8 in the Acid/Base sereisNeed help with orgo? Download my free guide '10 Secrets... A step-by-step explanation of how to draw the HCO3- Lewis Dot Structure (Hydrogen Carbonate or Bicarbonate Ion).For the HCO3- structure use the periodic tabl... In order to balance H2O2 = O2 + H2O you'll need to watch out for two things. First, be sure to count all of H and O atoms on each side of the chemical equat... my name is jeff. Skip navigation About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators ... This video defines and compares the Arrhenius and Bronsted-Lowry acid and base theories. Then it provides examples for identifying the movement of protons (hydrogen ions) and conjugate acid and bas... 0:25this ion hydrogen atom has one valence ... Identify Conjugate Acid Base Pairs (Bronsted Lowry) - Duration: 6:04. chemistNATE 533,762 views. 6:04. Calculating CO32- Formal Charges: Calculating ...
Copyright © 2024 hot.realmoneygame.xyz